

Highlight
Long-Distance Distributed Opitical Fiber Sensing Technology
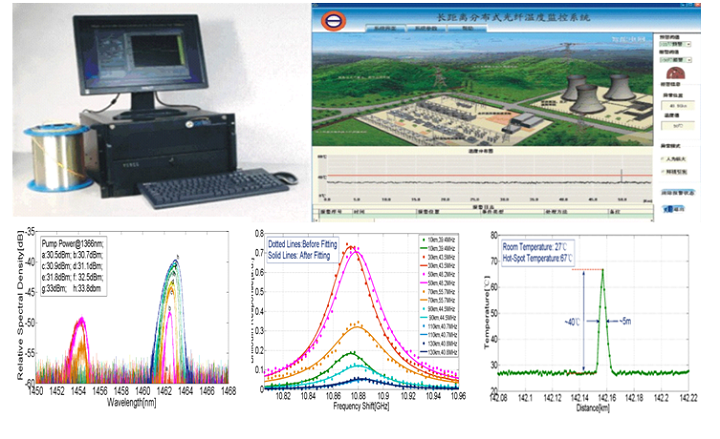
Distributed optical fiber sensing integrates sensing and transmission, owning many advantages such as anti-electromagnetic interference, space continuous detection, high sensitivity and no power supply. It is especially suitable for the cases requiring long distance, high precision, high spatial resolution, and has become the research frontier and hot issue for several years in optical fiber sensing.
The research is supported by key projects of Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61290312), mainly focus on the technologies and relative mechanisms of ultra-long-distance fiber-optic distributed sensing system based on Brillouin optical time domain analysis (BOTDA) and phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (Φ-OTDR) ,striving to solve problems restricted by SNR deterioration in the long distance distributed optical fiber sensing system, such as sensing distance, measurement accuracy and spatial resolution. We firstly propose the new scheme of distributed optical amplification based on random fiber laser and ultra-long ring fiber laser and applied it to long distance BOTDA. Combined with optical pulse coding technology, we have achieved 142km full free relay distributed sensing, the sensing accuracy is better than ± 1.5 ℃and the spatial resolution isup to 5m. Furthermore, we apply the wavelet transform and SNR enhanced technology of distributed optical amplification to long distance Φ-OTDR, achieving138 km full free relay sensing with spatial resolution better than 15m. This is currently the best performance of such fiber optic sensors internationally.
Our research also involves the characteristics and mechanisms of random lasers based on special optical fiber, low threshold and high order random lasers. The relative outcomes have been published in International optical top journals, such as Optics Express.
The research is supported by key projects of Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61290312), mainly focus on the technologies and relative mechanisms of ultra-long-distance fiber-optic distributed sensing system based on Brillouin optical time domain analysis (BOTDA) and phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (Φ-OTDR) ,striving to solve problems restricted by SNR deterioration in the long distance distributed optical fiber sensing system, such as sensing distance, measurement accuracy and spatial resolution. We firstly propose the new scheme of distributed optical amplification based on random fiber laser and ultra-long ring fiber laser and applied it to long distance BOTDA. Combined with optical pulse coding technology, we have achieved 142km full free relay distributed sensing, the sensing accuracy is better than ± 1.5 ℃and the spatial resolution isup to 5m. Furthermore, we apply the wavelet transform and SNR enhanced technology of distributed optical amplification to long distance Φ-OTDR, achieving138 km full free relay sensing with spatial resolution better than 15m. This is currently the best performance of such fiber optic sensors internationally.
Our research also involves the characteristics and mechanisms of random lasers based on special optical fiber, low threshold and high order random lasers. The relative outcomes have been published in International optical top journals, such as Optics Express.
